Below you will find pages that utilize the taxonomy term “Devops”
The Tech Chorus DevOps Platform
The Tech Chorus DevOps Platform
Over the last decade, the way we develop and deploy software has transformed significantly. This transformation has brought together various sub-disciplines, collectively known as DevOps engineering, including:
- IT Engineering: Focused on hardware and networking infrastructure.
- System Administration: Responsible for managing servers in racks, data centers, or colocation services.
- Cloud Infrastructure Engineering: Specializes in managing public cloud infrastructure.
- Platform Engineering: Builds and maintains platforms for deploying software applications, abstracting away complexity for users.
Introducing the Tech Chorus DevOps Platform
The Tech Chorus DevOps Platform is both a framework and software platform designed to host and run software applications and services. It facilitates the creation of cloud-based infrastructure from scratch and adheres to an opinionated approach, integrating best practices and tradeoffs. The platform offers a reference architecture and implementation to meet the most common use cases, with a strong emphasis on open-source technologies.
Kubernetes RBAC Objects For Cluster Administration
In a previous series of blog posts, we discussed the Kubernetes objects typically used to run a web application. We covered, Namespace, Pod, ConfigMap, Secret, Service, Deployment, ServiceAccount, Ingress, PDB, HPA, PV, PVC, Job and CronJob.
In this post, we will discuss some fundamental building blocks for the Kubernetes cluster administration: RBAC objects.
In most situations, Kubernetes API server is started with the flag --authorization-mode=RBAC which enables RBAC in
the cluster.
Automating Virtual Machine Installation Using libvirt, virsh And cloud-init
Introduction
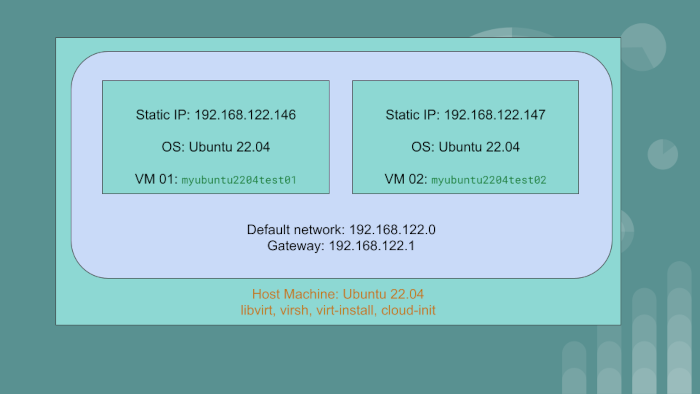
We have the host machine with the OS Ubuntu 22.04. On this PC or server, we will create two virtual machine guests:
myubuntu2204test01having static IP of192.168.122.146myubuntu2204test02having static IP of192.168.122.147
The guest VMs will use the default network created by libvirt. The gateway IP for the default network
is 192.168.122.1.
We will achieve automation using libvirt, qemu and cloud-init. To go through the article and exercise,
you should have a rudimentary understanding of Linux system administration and networking.
Linux KVM Bridge
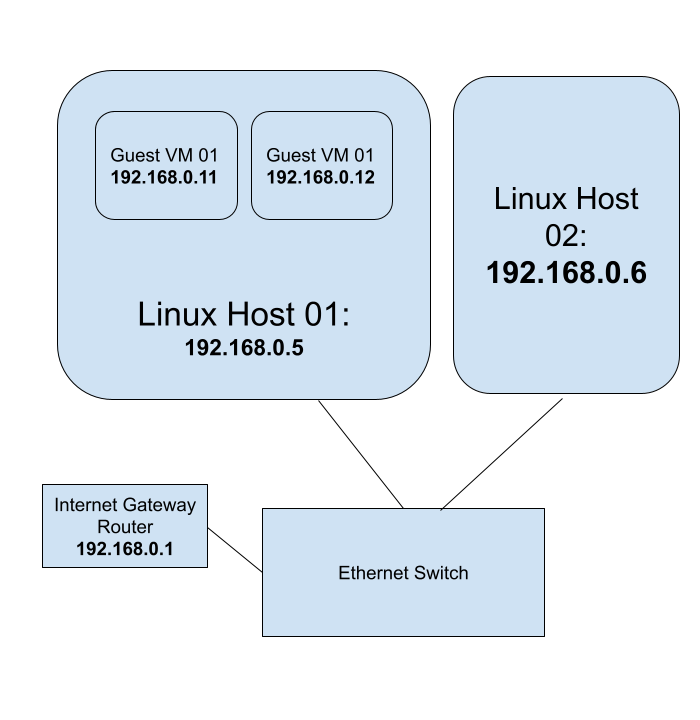
Using Linux KVM, Expose Virtual Guests On The LAN
Audience: The blog post is for beginner to intermediary Linux system administrators.
- You should have a thorough understanding of the shell commands and
- be comfortable on the command line
- be able to install and configure packages, etc.
- be able to start and stop services using
systemd - be familiar with Linux configuration files
- be able to set Linux kernel parameters using
sysctl - be able to enable and disable Kernel modules
- be comfortable installing and using guest VMs using
libvirt
You should have a rudimentary understanding of networking concepts and tooling such as
Ansible Naming Conventions
Purpose Of Having Naming Conventions For An Ansible Project
- Consistency: Adopting a naming convention standardizes naming across the project and organization. This makes it easier for developers to switch between projects. Typically, an organization with an infrastructure team will have several Ansible projects and source code repositories. A developer working on one such Ansible project can seamlessly switch to another given a standard naming convention.
- Error Reduction: With improper naming there can be pitfalls. For instance, using hyphens(
-) in variable names can cause parsing errors since Ansible might interpret them as the minus operator. Standardizing naming for variables can help avoid collisions. - Readability: With a standard naming convention, it helps developers to find variables, files and tasks quickly.
Naming Conventions For Ansible Roles And Playbooks
- Role name : use lowercase letters and hyphens to separate words: For example,
web-serverordatabase-backup. - Task file name: user lowercase letters and underscores to separate words. When statements such as include
are used, it is convenient to have file names without hyphens. For example:
install_web_ubuntu.yml - YAML file extension:
ymlinsteadyaml. To be consistent and succinct. - Task name: start with a verb: Use an action verb at the beginning of the task name to indicate what the role does. For example, Install Nginx or Configure firewall. Start with a capital letter. No need to end with a period for a few words of task description.
- Variable name: lowercase letters and underscores to separate words. The variable must start with the role
name. For example, if the role name is nginx, the variable name should be
nginx_default_hostname.
Content Guide
- Always include a README file for the role. Describe in detail how to use the role. Create a table to show the role variables and their defaults.
- Include automated tests using Molecule.
The Ansible Learning Path
Ansible Prerequisites
Before jumping on to learning Ansible, have a firm grounding in Linux system administration and shell scripting. You can use Ansible for a lot of automation projects. The primary target audience for this blog post are DevOps engineers, IT infrastructure engineers and system administrators who create and manage IT infrastructure to run workloads. A good understanding of YAML is required before starting to write Ansible playbooks. A background in at least one programming language helps. Python programing is not a requirement per se. But Python programming familiarity helps put together some automated testing.
DevOps Lab: Create Your Own Kubernetes Cluster
Architecture 1: Kubernetes Control Plane Without HA
Create three Virtual Machine guests on your laptop or workstation.
VM 01- Kubernetes Control PlaneVM 02, VM 03- Kubernetes Worker nodes
Architecture 2: Kubernetes Control Plane With HA
Create five Virtual Machine guests on your laptop or workstation.
VM 01, VM 02, VM 03- Kubernetes Control Plane with HAVM 04, VM 05- Kubernetes Worker nodes
Use the Kubeadm tool to create the cluster.
DevOps Lab: Create Your Own Reference Application
A reference application is a sample application that is used as a guide for developers to learn and implement best practices for software development, testing, deployment, and operations within a specific technology stack or framework. It can serve as a blueprint for building and maintaining similar applications and can be used to demonstrate the use of tools, processes, and techniques for achieving high levels of automation, scalability, and reliability.
If you are learning how to deploy applications to Kubernetes of Virtual Machines in cloud, create your own tiny application.
Kubernetes Objects Required For A Typical Web Application: Part II
In the Kubernetes Objects Required For A Typical Web Application post we talked about few Kubernetes objects that a web application developer should get accustomed to. In this post, we will extend the series and talk about more objects that can help web developers scale their applications.
As we delve deeper into Kubernetes topics, the demarcation of roles and skill sets start to reveal. In larger organizations, a dedicated team of infrastructure engineers design and make choices of network topology, IAC tooling and orchestration of the Kubernetes clusters and CI/CD pipelines. Typically, such DevOps engineers manage scaling and storage by installing the required controllers and CSI drivers. Application developers whose applications are deployed on the cluster maybe able to tune certain parameters of certain objects to manage the scaling needs of their applications. Depending on the situation, the developers maybe able to request and use storage volumes with certain restrictions. Regardless of the organization’s team structure, you should be able to learn about these Kubernetes concepts and objects and play with them locally on your laptop using Minikube.
SOPS To Manage Secrets In Git Repositories
In a previous post, we discussed using age to manage secrets in Git repositories.
In this post, let’s improve our secrets management workflow in Git repositories using SOPS.
sops is an editor of encrypted files that supports popular configuration formats such as YAML and various encryption
techniques such as age.
Read the blog post about age to install the package and creating the key file.
This time, we will use sops to perform encryption and decryption operations instead of the age command.
Linux virtualization
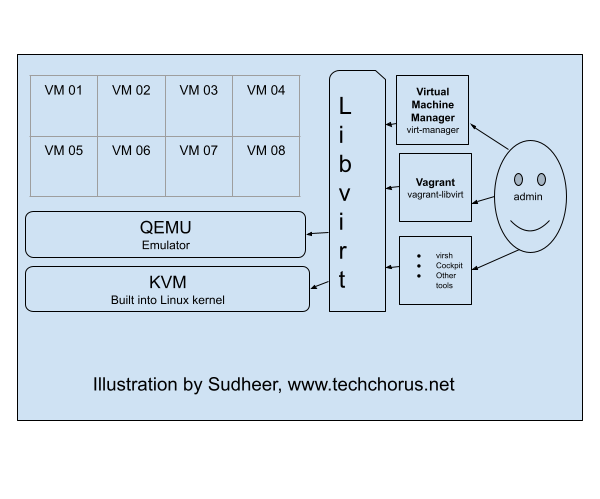
KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine), libvirt, and QEMU are three components that work together to provide a
virtualization solution on Linux systems.
KVM is a virtualization infrastructure built into the Linux kernel that allows it to run multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical host. It provides the underlying virtualization technology, such as hardware acceleration for virtualized CPU and memory, and device emulation.
DevOps Lab: Run Your Own File Server
NFS Server
To run your own NFS (Network File System) server, you’ll need to first install Linux on your server. I’d go with
Debian, Ubuntu or CentOS distributions. Once you’ve done that, you can install the NFS server software, which is
typically included with most Linux distributions. After the NFS server software is installed, you’ll need to configure
it to specify which directories on the server should be shared with NFS clients, and what type of access they should
have. This typically involves editing the server’s configuration file, which is typically located at /etc/exports.
Once the server is configured, you can start the NFS server and begin sharing files with NFS clients. To access the
shared files, the NFS clients will need to mount the NFS share using the mount command.
DevOps Lab: Run Your Own VPN Server
There are many applications and technologies enabled by VPN. We will focus on one of them in this post: client VPN.
Connecting To A Private Network
If the server you are trying to access is on a private network, you can use a VPN to connect to the network as if you were physically present on the same network. This can be useful if you need to access resources or devices that are only available on the private network.
DevOps Lab: Run Your Own Log Server
syslog
Syslog is a standard for logging system events on Unix and Linux systems. It is typically used to collect and store log messages from various applications and system components, such as the kernel, system libraries, and applications. Syslog uses a client-server model, where each client application sends log messages to a central syslog server, which then stores the messages in a log file. The syslog server can also forward the log messages to other syslog servers or send them to a log management system for further analysis. Syslog uses a simple text-based format for its log messages, which makes it easy to read and analyze. It also supports multiple levels of severity, allowing applications to categorize their log messages based on importance.
DevOps Lab: Run Your Own Monitoring Server
There are many tools and software programs that can be used for monitoring and performance analysis on Linux systems. Some popular options include:
- top - This is a command-line utility that shows real-time information about the processes running on a Linux system, such as their CPU and memory usage.
- htop - This is a more advanced version of top that provides a more user-friendly interface and additional features, such as the ability to sort processes by different metrics and to kill processes.
- sar - This is a command-line utility that collects and displays performance metrics for a Linux system over time. It can be used to analyze CPU, memory, I/O, and network usage, as well as other metrics.
- iostat - This is a command-line utility that shows real-time information about I/O performance on a Linux system. It can be used to monitor the performance of disks and other storage devices.
- vmstat - This is a command-line utility that shows real-time information about various system resources, such as memory, CPU, and I/O. It can be used to monitor the overall health of a Linux system.
- netstat - This is a command-line utility that shows information about network connections on a Linux system. It can be used to monitor the status of network connections and to diagnose networking issues.
There are also many modern monitoring tools and software programs available for Linux, such as Prometheus and Zabbix. These tools typically offer more advanced features and capabilities than the built-in Linux utilities, such as the ability to collect and store metrics over time, and to generate alerts when certain conditions are met.
DevOps Lab: Run Your Own Email Server
To run your own email server using Linux and other open source software, you’ll need to first choose a Linux distribution and install it on your server. I’d go with either Ubuntu, Debian or Rocky Linux. Once you’ve done that, you can choose an email server software that is compatible with Linux, such as Postfix or Exim. After installing and configuring the email server software, you’ll need to set up DNS records and configure authentication and encryption to ensure that your email server is secure. Finally, you’ll need to test your email server to make sure it is working properly and can send and receive messages.
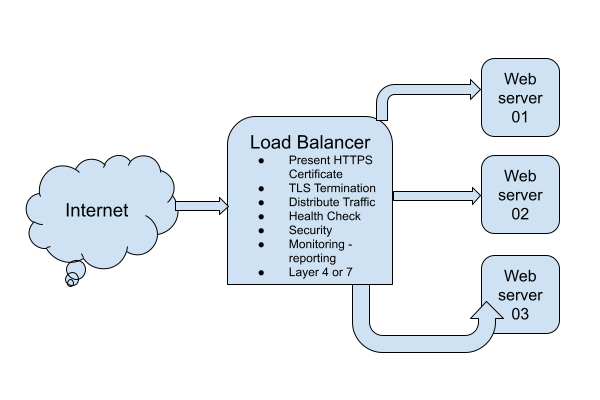
DevOps Lab: Run Your Own Load Balancer
Definition
A load balancer is a type of software or hardware that distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers or resources. This allows the load balancer to distribute the workload evenly, improving the performance and availability of the application.
The Load Balancer Lab
To run your own load balancer using open source software, you will need to:
- Install and configure the load balancer software on a server. Some popular open source options include HAProxy, Nginx, and Envoy.
- Configure the load balancer to distribute incoming traffic to the appropriate servers or resources. This typically involves setting up virtual servers and defining rules for routing traffic.
- Test the load balancer to ensure that it is working correctly and distributing traffic as expected.
- Monitor the load balancer and the underlying servers to ensure that the system is performing well and handling traffic effectively.
- Continually tune and optimize the load balancer configuration to improve performance and ensure that the application is always available and responsive.
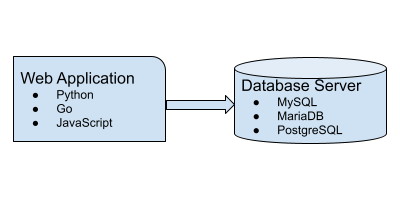
DevOps Lab: Run Your Own Database Server
Your web applications need a solution to store and retrieve its data. A relational database is often used in web applications. MySQL, MariaDB and PostgreSQL are some popular relational databases. There’s also SQLite. Many applications can use any of these relational databases by the virtue of the database layer abstraction. If you are writing your own web application, pick any one database and install it on your web server.
Install The Database
- Install the package.
- Enable and start the database
systemdunit. - Initialize the database server.
- Create databases.
- Create database users and set their passwords.
Connect The Web Application To The Database Server
Breaking Into DevOps: Training Tips
I see a lot of people are trying to break into software engineering and DevOps. There are many inspiring stories out there. People from other industries and verticals have switched to IT and are having a successful career. You can do it too.
Let us look at the resources available to you.
Online Vs. Offline Training And Learning Resources
Online
All you need to break into DevOps is:
DevOps Lab: Run Your Own Web Server
Once upon a time, Apache was the de-facto web server solution. Later, Nginx became popular. If you are getting started with DevOps and Linux system administration, I would recommend you to start with Nginx.
Start With A Static Website
What is a static website? A website made from HTML and CSS. And maybe some JavaScript, images, videos, fonts, etc. The
key takeaway is that there is no server side application involved. Install the Nginx web server on your Linux VM.
Configure it to serve a static website. You will need a static website as a per-requisite. Create a static website by
assembling some HTML, CSS, JavaScript and images. Optionally, add some fonts and videos. Access the website from your
web browser by typing the IP address of the web server in the address bar. Take it to the next level by pointing
the DNS A record of your domain to the VM. For our purposes, a fake domain or a local unregistered domain is
sufficient. Manipulating /etc/hosts is also fine. Enjoy viewing the website from the browser.
Age To Encrypt Secrets
Are you storing secrets such as database credentials, API keys, etc. unencrypted in Git repositories? Stop.
To protect your secrets, do not store them anywhere unencrypted. Especially in Git repositories. Ideally, your organization must have some vault solution where secrets can be stored and securely shared with people on a need-to-know basis. In many small organizations, having such a central secrets management solution is still a luxury. The need to store such secret information in Git repositories is obvious. There are a few ways in which you can encrypt secrets. We discussed using Ansible Vault in one of the previous blog posts.
Kubernetes Objects Required For A Typical Web Application: Part I
From an application developer and Kubernetes user’s point of view, you have to have a working knowledge of Kubernetes. The post outlines the most important Kubernetes objects required to deploy a typical web application. Let us assume that the web application uses the two-tier architecture. We also assume that the cluster is created and administered by an infrastructure or DevOps engineer and the necessary access is provided to the developer to deploy their web application onto the Kubernetes cluster. The Kubernetes operations are performed from the web application developer’s perspective.
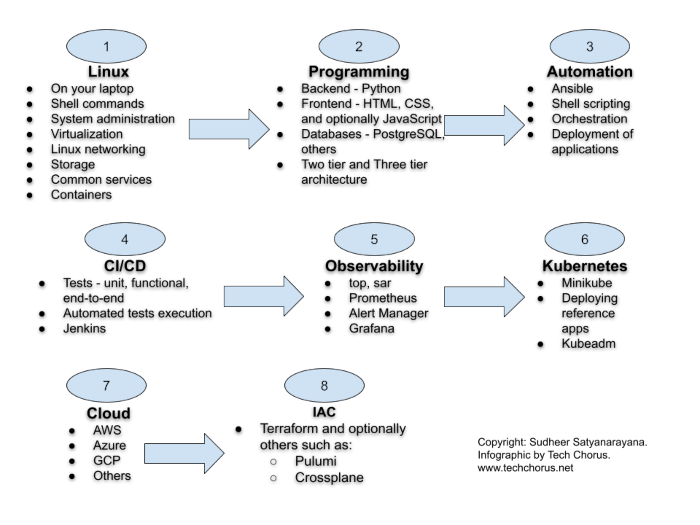
Learning Linux For DevOps
Introduction
If you have chosen the DevOps engineering path for your career, Linux system administration skills are a must. Companies run their workloads on Linux on-premise as well as in the cloud. Many developers write software on their Linux laptops and workstations. In this post, I will lay out a plan to master Linux system administration skills. The journey begins with you becoming a Linux desktop user. Gradually, you start using your laptop as a Linux server. Become more productive and create your own labs using virtualization. You will be able to simulate a lot of Linux infrastructure scenarios on your laptop.
The DevOps Path
- Learn Linux. Install Linux on your laptop. Get familiar with Linux commands. Learn virtualization. Unlock the path to learn more Linux.
- Programming. Acquiring some programming skills using a general purpose programming language like Python goes a long way. Learning some web development is required in most DevOps engineering contexts. Although you don’t have to be an expert in web development, you should have a clear understanding of workloads consisting of web applications and microservices. Learning some HTML, CSS and JavaSript is required for web development. At this point, you have to learn at least one database system. I recommend PostgreSQL to get started with relational database system. Git is also an essential tool to manage source code.
- Automation is the cornerstone of DevOps engineering. Learn the basics of automation with Ansible and shell scripting.
- CI/CD. The purpose of DevOps is to create a culture and practice where developers can ship their applications
to customers quickly, safely and continuously. The
CI/CDpipelines often constitute the backbone of the DevOps practice. Jenkins is a popular tool to createCI/CDpipelines. Learn the basics of Jenkins and create pipelines to automatically test and deploy applications. - Observability and monitoring. Start with Linux commands such as
top,free,duand progress towards Prometheus. The typical Prometheus stack includes Alert Manager and Grafana. Then explore the world of traces with tools such as Jaeger and OpenTelemetry. - Kubernetes. The quintessential container orchestration platform.
- Cloud engineering. Start with one of the popular clouds such as
AWS,AzureorGCP. - IAC. Take automation to the next level in the cloud. Use Terraform to orchestrate resources in the cloud.
Tech Chorus References
- Learning Linux For Devops
- Preparing For A DevOps Engineer Job With A Personal Project
- Three Day Plan To Learn Git
Learning Resources
DevOps
- Coursera Course: Google IT Automation with Python Professional Certificate
- Crash Course On Python
- Using Python to Interact with the Operating System
- Introduction to Git and GitHub
- Troubleshooting and Debugging Techniques
- Configuration Management and the Cloud
- Automating Real-World Tasks with Python
Python
- Free interactive Python tutorial: LearnPython.org
DevOps Lab: Run Your Own DNS Server
As soon as you are ready to deploy services and applications on the Internet, the first thing you need is a registered domain and a DNS server. Often people just use the DNS service provided by the domain registrar or the hosting or cloud provider. Using the managed service is not a requirement. You can host your own DNS server and manage the DNS for your domains. There are many open source software using which you can build your own DNS servers. Bind is the traditional and probably the most popular DNS solution out there. There are other options such as Knot, PowerDNS and Unbound.
Sysctl
Introduction
The Linux Kernel parameters are settings that can be configured to control the behavior of the Linux kernel. They are typically used to fine-tune system performance or to enable/disable certain features.
Some examples of kernel parameters include:
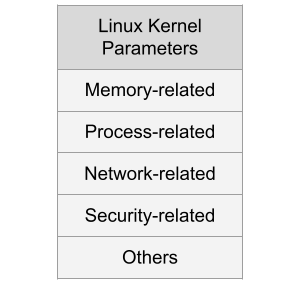
Memory-related parameters: These parameters control how the kernel manages system memory, including how much memory is allocated to user processes and how aggressively the kernel caches data.
Processor-related parameters: These parameters control how the kernel interacts with the system’s processors, including how it schedules processes and how it handles interrupts.
Jenkins And Ansible: A Get Together
If you are wondering how to automate the installation and configuration of Jenkins using code, this post is for you.
Jenkins is a popular open source tool to build CI/CD pipelines.
Ansible is a popular open source tool to automate a lot of things in IT, including CI/CD and infrastructure orchestration.
Ansible can be used to deploy applications in the cloud. Ansible is a nice tool to execute steps such as:
Preparing For A DevOps Engineer Job With A Personal Project
The blog post attempts to answer some questions like:
- How to become a DevOps engineer?
- How to prepare for a DevOps engineer interview?
- How to get a DevOps engineer job?
In a previous blog post, I wrote about the path an aspiring DevOps engineer could follow.
In this blog post, I will lay out a concrete plan using which you can prepare yourself for a DevOps engineer job. If you follow the steps carefully, you will be armed with practical DevOps knowledge, and you will be able to apply for DevOps engineer jobs confidently.
From Build And Deploy Engineer To DevOps Engineer
The build and deploy engineer is a role in IT/infrastructure/devops teams of organizations that is responsible for deploying a set of applications using CI/CD pipelines. Usually, they use the pipelines, tools and processes created by DevOps engineers, consultants or practitioners. They tweak things with tools like Ansible, Jenkins, Git, Maven, etc. here and there a bit.
Are you one such build and deploy engineer looking to transition your career into DevOps engineering? Here’s a path you could follow:
Tech Chorus Blog Hosting Story
The Tech Chorus blog, started by Sudheer Satyanarayana in 2008, has evolved through various hosting technologies and software over the years. This post captures that journey, highlighting the transitions, challenges, and decisions that shaped its infrastructure.
The Early Days: Drupal and LAMP
Back in the day, the blog ran on the Drupal content management system (CMS), a popular choice among developers. The LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP) stack dominated web hosting at the time, and Drupal was one of my favorite CMSes. The site was hosted on a cPanel server, making management relatively straightforward.
Run Your Own OpenVPN Server
Introduction
The article explains how to run your own OpenVPN server. We will create a Certificate Authority Server and an OpenVPN server. We will also generate certificates for the clients. We will also learn how to manage revocation of client certificates using the Ansible roles.
Use the Ansible roles gavika.openvpn and gavika.easy_rsa to install and configure your OpenVPN server.
You can install the OpenVPN server on any public cloud or hosting provider or on-premise servers. The Ansible roles
are designed to install the OpenVPN server and a Certificate Authority server.
Installing AWS CloudWatchAgent On EC2 Instance Via Ansible
Install the Ansible role gavika.aws_cloudwatchagent via Galaxy
ansible-galaxy install gavika.aws_cloudwatchagent
Create The Playbook File - cw-play.yml :
---
- hosts: all
become: true
vars:
roles:
- role: gavika.aws_cloudwatchagent
Prepare the AWS CloudWatch Agent configuration
In your variables file, use aws_cloudwatch_agent_config
agent:
metrics_collection_interval: 60
run_as_user: "cwagent"
metrics:
namespace: "Gavika"
append_dimensions:
InstanceId: "${aws:InstanceId}"
metrics_collected:
disk:
measurement:
- used_percent
metrics_collection_interval: 60
resources:
- "*"
mem:
measurement:
- mem_used_percent
metrics_collection_interval: 60
In this example, I am using the namespace, Gavika. Feel free to change it. We collect the cpu, disk, diskio,
mem and swap metrics. The agent will send these metrics once in 360 seconds.
PostgreSQL Cheatsheet
Install PostgreSQL Server
Fedora and CentOS:
sudo dnf install postgresql-server
Ubuntu 18.04:
sudo apt install postgresql
New Server Initialization
On CentOS 7/Fedora 30:
sudo postgresql-setup initdb
Upgrading From An Older Version
sudo postgresql-setup --upgrade
Administering The Database Server
Managing The postgresql Daemon
Starting PostgreSQL server
sudo systemctl start postgresql
Checking PostgreSQL Server Status:
sudo systemctl status postgresql
Enabling PostgreSQL Server Systemd Unit/Enabling PostgreSQL Server On Boot:
sudo systemctl enable postgresql
Allowing Password Based Login From localhost
Edit /var/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.conf as privileged user(root) and add this line: