Below you will find pages that utilize the taxonomy term “Devops Lab”
DevOps Lab: Create Your Own Kubernetes Cluster
Architecture 1: Kubernetes Control Plane Without HA
Create three Virtual Machine guests on your laptop or workstation.
VM 01- Kubernetes Control PlaneVM 02, VM 03- Kubernetes Worker nodes
Architecture 2: Kubernetes Control Plane With HA
Create five Virtual Machine guests on your laptop or workstation.
VM 01, VM 02, VM 03- Kubernetes Control Plane with HAVM 04, VM 05- Kubernetes Worker nodes
Use the Kubeadm tool to create the cluster.
DevOps Lab: Create Your Own Reference Application
A reference application is a sample application that is used as a guide for developers to learn and implement best practices for software development, testing, deployment, and operations within a specific technology stack or framework. It can serve as a blueprint for building and maintaining similar applications and can be used to demonstrate the use of tools, processes, and techniques for achieving high levels of automation, scalability, and reliability.
If you are learning how to deploy applications to Kubernetes of Virtual Machines in cloud, create your own tiny application.
DevOps Lab: Run Your Own File Server
NFS Server
To run your own NFS (Network File System) server, you’ll need to first install Linux on your server. I’d go with
Debian, Ubuntu or CentOS distributions. Once you’ve done that, you can install the NFS server software, which is
typically included with most Linux distributions. After the NFS server software is installed, you’ll need to configure
it to specify which directories on the server should be shared with NFS clients, and what type of access they should
have. This typically involves editing the server’s configuration file, which is typically located at /etc/exports.
Once the server is configured, you can start the NFS server and begin sharing files with NFS clients. To access the
shared files, the NFS clients will need to mount the NFS share using the mount command.
DevOps Lab: Run Your Own VPN Server
There are many applications and technologies enabled by VPN. We will focus on one of them in this post: client VPN.
Connecting To A Private Network
If the server you are trying to access is on a private network, you can use a VPN to connect to the network as if you were physically present on the same network. This can be useful if you need to access resources or devices that are only available on the private network.
DevOps Lab: Run Your Own Log Server
syslog
Syslog is a standard for logging system events on Unix and Linux systems. It is typically used to collect and store log messages from various applications and system components, such as the kernel, system libraries, and applications. Syslog uses a client-server model, where each client application sends log messages to a central syslog server, which then stores the messages in a log file. The syslog server can also forward the log messages to other syslog servers or send them to a log management system for further analysis. Syslog uses a simple text-based format for its log messages, which makes it easy to read and analyze. It also supports multiple levels of severity, allowing applications to categorize their log messages based on importance.
DevOps Lab: Run Your Own Monitoring Server
There are many tools and software programs that can be used for monitoring and performance analysis on Linux systems. Some popular options include:
- top - This is a command-line utility that shows real-time information about the processes running on a Linux system, such as their CPU and memory usage.
- htop - This is a more advanced version of top that provides a more user-friendly interface and additional features, such as the ability to sort processes by different metrics and to kill processes.
- sar - This is a command-line utility that collects and displays performance metrics for a Linux system over time. It can be used to analyze CPU, memory, I/O, and network usage, as well as other metrics.
- iostat - This is a command-line utility that shows real-time information about I/O performance on a Linux system. It can be used to monitor the performance of disks and other storage devices.
- vmstat - This is a command-line utility that shows real-time information about various system resources, such as memory, CPU, and I/O. It can be used to monitor the overall health of a Linux system.
- netstat - This is a command-line utility that shows information about network connections on a Linux system. It can be used to monitor the status of network connections and to diagnose networking issues.
There are also many modern monitoring tools and software programs available for Linux, such as Prometheus and Zabbix. These tools typically offer more advanced features and capabilities than the built-in Linux utilities, such as the ability to collect and store metrics over time, and to generate alerts when certain conditions are met.
DevOps Lab: Run Your Own Email Server
To run your own email server using Linux and other open source software, you’ll need to first choose a Linux distribution and install it on your server. I’d go with either Ubuntu, Debian or Rocky Linux. Once you’ve done that, you can choose an email server software that is compatible with Linux, such as Postfix or Exim. After installing and configuring the email server software, you’ll need to set up DNS records and configure authentication and encryption to ensure that your email server is secure. Finally, you’ll need to test your email server to make sure it is working properly and can send and receive messages.
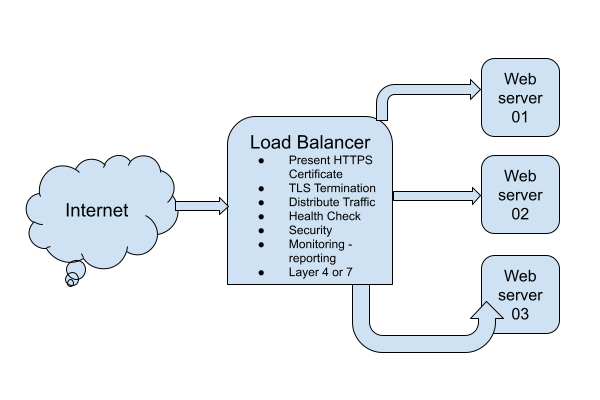
DevOps Lab: Run Your Own Load Balancer
Definition
A load balancer is a type of software or hardware that distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers or resources. This allows the load balancer to distribute the workload evenly, improving the performance and availability of the application.
The Load Balancer Lab
To run your own load balancer using open source software, you will need to:
- Install and configure the load balancer software on a server. Some popular open source options include HAProxy, Nginx, and Envoy.
- Configure the load balancer to distribute incoming traffic to the appropriate servers or resources. This typically involves setting up virtual servers and defining rules for routing traffic.
- Test the load balancer to ensure that it is working correctly and distributing traffic as expected.
- Monitor the load balancer and the underlying servers to ensure that the system is performing well and handling traffic effectively.
- Continually tune and optimize the load balancer configuration to improve performance and ensure that the application is always available and responsive.
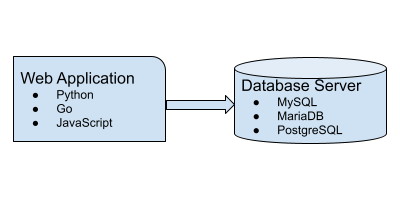
DevOps Lab: Run Your Own Database Server
Your web applications need a solution to store and retrieve its data. A relational database is often used in web applications. MySQL, MariaDB and PostgreSQL are some popular relational databases. There’s also SQLite. Many applications can use any of these relational databases by the virtue of the database layer abstraction. If you are writing your own web application, pick any one database and install it on your web server.
Install The Database
- Install the package.
- Enable and start the database
systemdunit. - Initialize the database server.
- Create databases.
- Create database users and set their passwords.
Connect The Web Application To The Database Server
DevOps Lab: Run Your Own Web Server
Once upon a time, Apache was the de-facto web server solution. Later, Nginx became popular. If you are getting started with DevOps and Linux system administration, I would recommend you to start with Nginx.
Start With A Static Website
What is a static website? A website made from HTML and CSS. And maybe some JavaScript, images, videos, fonts, etc. The
key takeaway is that there is no server side application involved. Install the Nginx web server on your Linux VM.
Configure it to serve a static website. You will need a static website as a per-requisite. Create a static website by
assembling some HTML, CSS, JavaScript and images. Optionally, add some fonts and videos. Access the website from your
web browser by typing the IP address of the web server in the address bar. Take it to the next level by pointing
the DNS A record of your domain to the VM. For our purposes, a fake domain or a local unregistered domain is
sufficient. Manipulating /etc/hosts is also fine. Enjoy viewing the website from the browser.
DevOps Lab: Run Your Own DNS Server
As soon as you are ready to deploy services and applications on the Internet, the first thing you need is a registered domain and a DNS server. Often people just use the DNS service provided by the domain registrar or the hosting or cloud provider. Using the managed service is not a requirement. You can host your own DNS server and manage the DNS for your domains. There are many open source software using which you can build your own DNS servers. Bind is the traditional and probably the most popular DNS solution out there. There are other options such as Knot, PowerDNS and Unbound.