Below you will find pages that utilize the taxonomy term “Libvirt”
Automating Virtual Machine Installation Using libvirt, virsh And cloud-init
Introduction
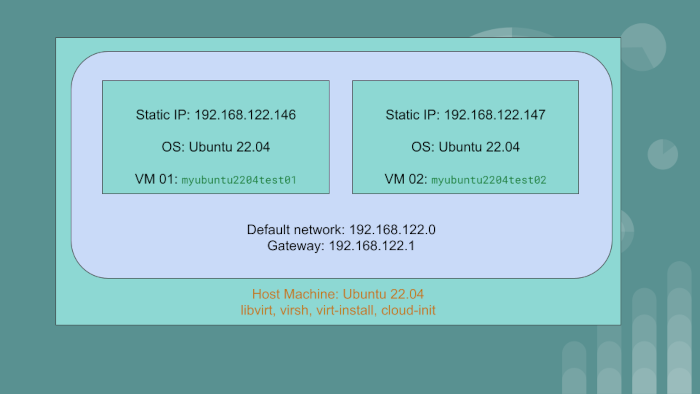
We have the host machine with the OS Ubuntu 22.04. On this PC or server, we will create two virtual machine guests:
myubuntu2204test01having static IP of192.168.122.146myubuntu2204test02having static IP of192.168.122.147
The guest VMs will use the default network created by libvirt. The gateway IP for the default network
is 192.168.122.1.
We will achieve automation using libvirt, qemu and cloud-init. To go through the article and exercise,
you should have a rudimentary understanding of Linux system administration and networking.
Linux KVM Bridge
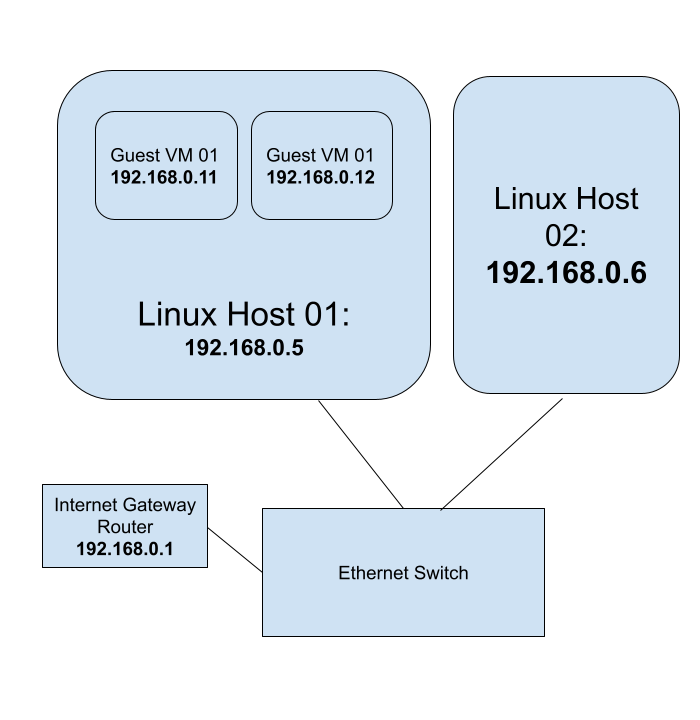
Using Linux KVM, Expose Virtual Guests On The LAN
Audience: The blog post is for beginner to intermediary Linux system administrators.
- You should have a thorough understanding of the shell commands and
- be comfortable on the command line
- be able to install and configure packages, etc.
- be able to start and stop services using
systemd - be familiar with Linux configuration files
- be able to set Linux kernel parameters using
sysctl - be able to enable and disable Kernel modules
- be comfortable installing and using guest VMs using
libvirt
You should have a rudimentary understanding of networking concepts and tooling such as
Linux virtualization
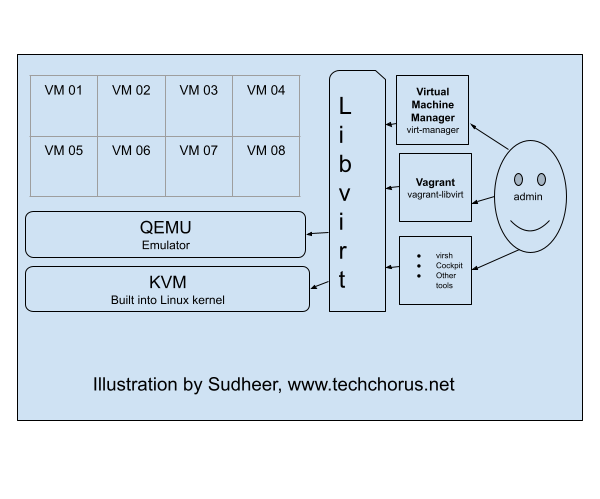
KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine), libvirt, and QEMU are three components that work together to provide a
virtualization solution on Linux systems.
KVM is a virtualization infrastructure built into the Linux kernel that allows it to run multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical host. It provides the underlying virtualization technology, such as hardware acceleration for virtualized CPU and memory, and device emulation.